A complete guide to wood structure screws: From material selection to installation
 2025.09.08
2025.09.08
 Industry news
Industry news
1. Introduction
Wood structures are widely used in construction and furniture manufacturing. From log cabins and patios to tables, chairs, and cabinets, they all require strong joints. Among the many fasteners, wood structural screws, with their strength, reliability, and repeatability, have gradually replaced traditional nails as the preferred method.
Compared to ordinary nails, screws provide stronger holding power, reducing the risk of wood cracking, and are more convenient for repairs or disassembly. For woodworkers striving for structural stability and durability, understanding the types of wood structural screws, selection tips, and proper installation methods is essential.
2. Classification and Characteristics of Wood Screws
Classification by Application
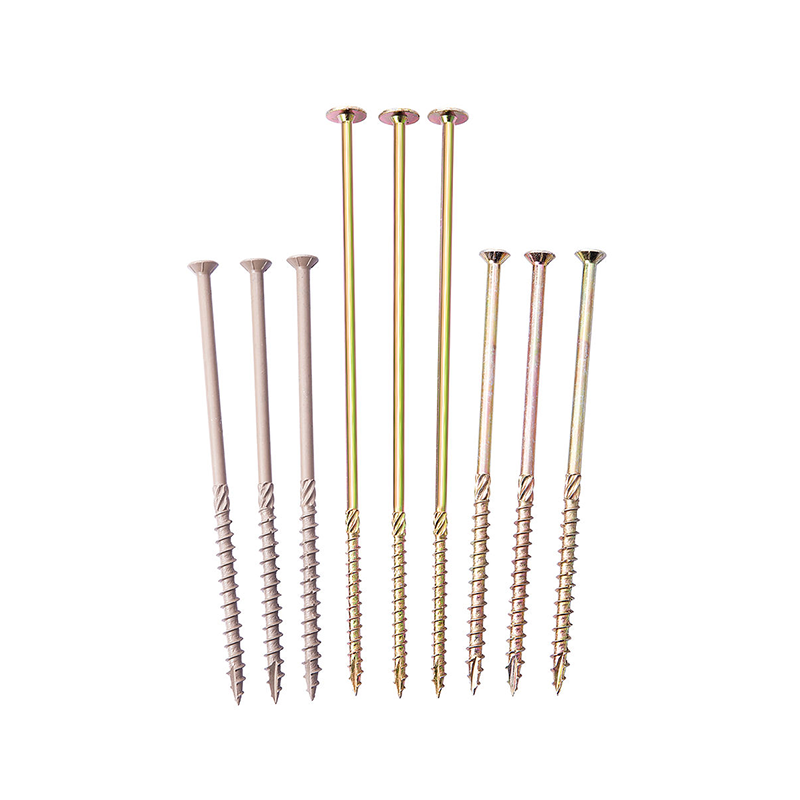
Furniture screws: Generally smaller in size and with a smooth finish, they are suitable for fine woodwork such as cabinets and chairs.
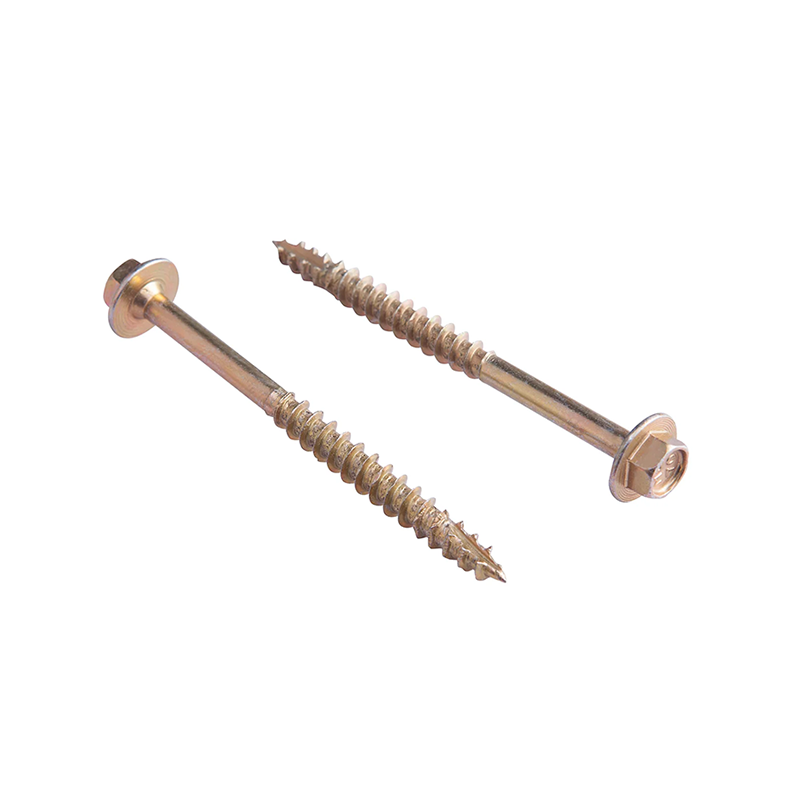
Building structural screws: Highly strong and long in length, they are used for large structures such as load-bearing beams and log cabin frames.
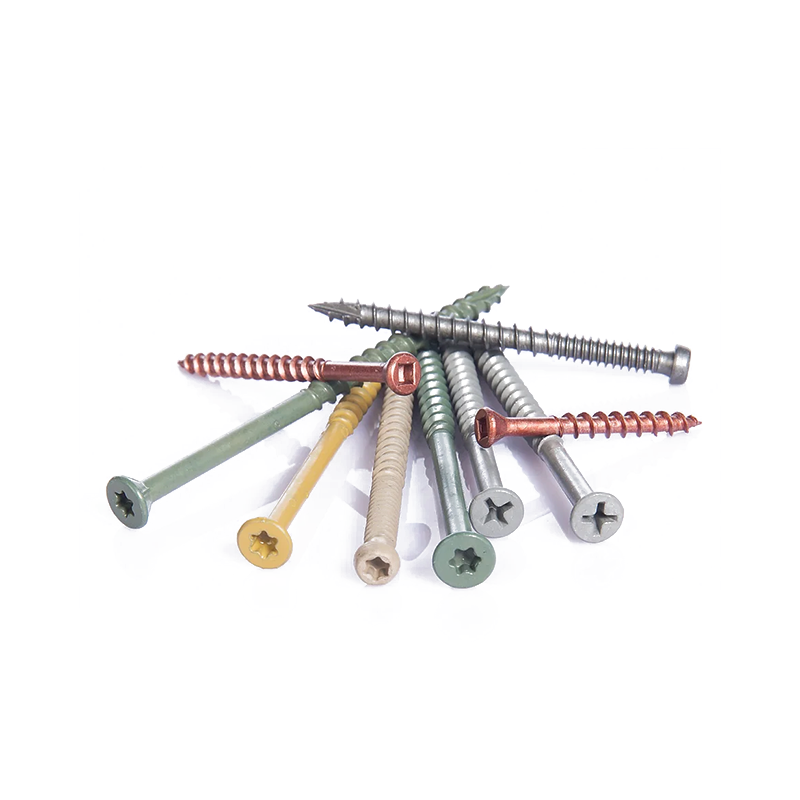
Outdoor anti-corrosion screws: Galvanized or coated to prevent rust and corrosion caused by rain and moisture, they are commonly used for decks, fences, and more. Classification by Head Shape
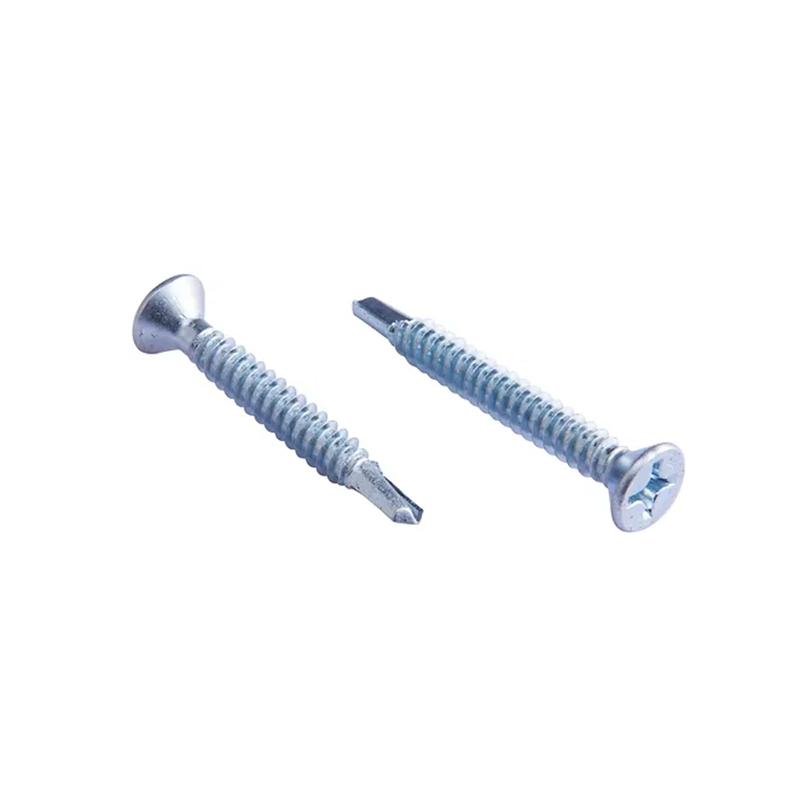
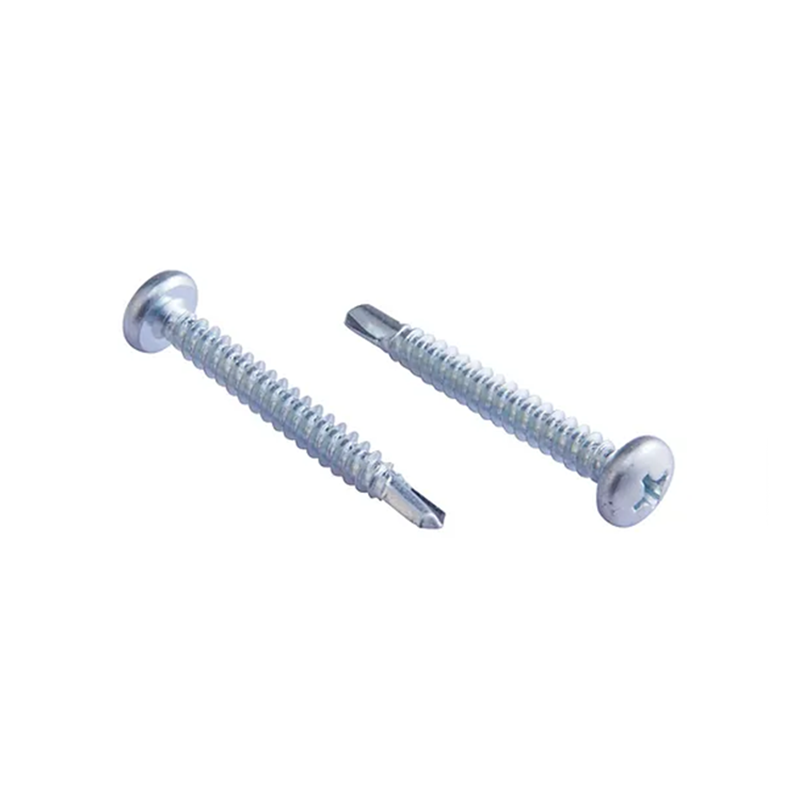
Countersunk head screws: These screws sit flush with the wood surface after being screwed in, and can even be recessed, making them suitable for applications requiring a smooth surface.
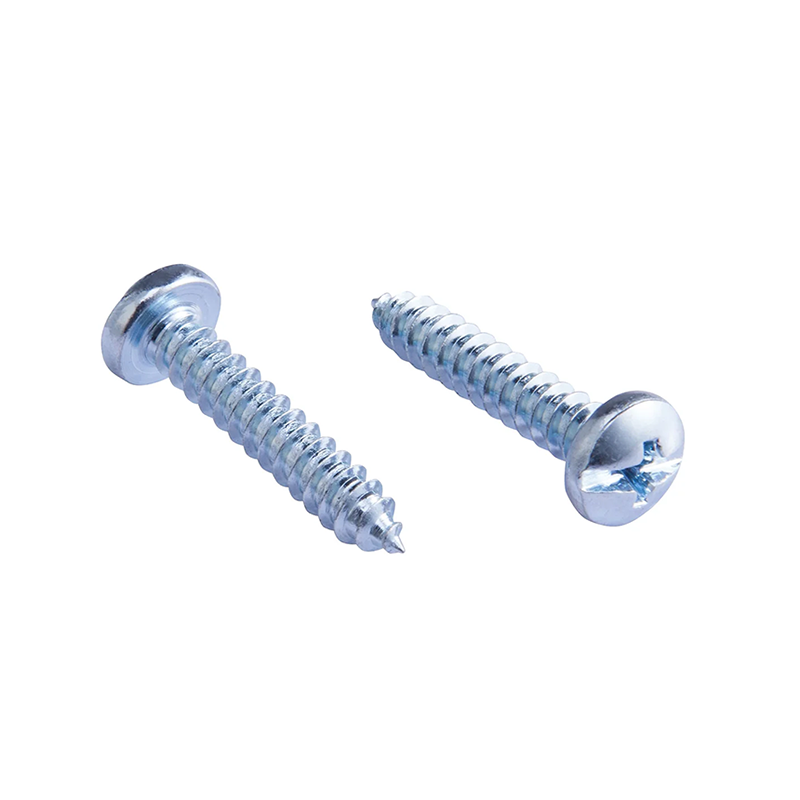
Round head screws: The head is exposed, offering a decorative touch and are commonly used in furniture assembly.
Hexagon head screws: Commonly used for load-bearing connections or those requiring high torque, suitable for quick tightening with power tools.
Classification by Material
Carbon steel screws: Common and economical, but prone to rust, they are mostly used indoors.
Stainless steel screws: Highly corrosion-resistant, particularly suitable for outdoor and humid environments.
Galvanized or coated screws: These screws have a rust-resistant surface treatment, offering a balance of cost-effectiveness and durability.
3. How to Choose the Right Screws for Wood Structures
Choose Based on Wood Hardness
Hardwoods (such as oak and walnut) require stronger screws with deeper threads.
Softwoods (such as pine and fir) can use standard screws, but be careful not to overtighten.
Choose Based on Wood Thickness
A general rule of thumb is to ensure adequate holding force: the screw length should be at least twice the thickness of the wood being fastened. Indoor vs. Outdoor Use
Indoor: Carbon steel or ordinary galvanized screws are sufficient.
Outdoor: Stainless steel or weather-resistant galvanized screws are recommended to prevent rust from affecting structural safety.
Corrosion Resistance and Load-Bearing Requirements
High-humidity environments: Stainless steel is preferred.
For heavy-load bearing structures: Choose large-diameter, long screws and use them with reinforcements.
4. Wood Screw Installation Tips
Pre-drilling and Countersinking
For hardwood or thick wood, pre-drilling holes can prevent cracking and make screw insertion easier.
When a flat surface is required, use a countersink drill bit to create a groove so that the screw head is flush with the wood or even slightly below the surface.
Tightening Tips
When using an electric screwdriver, control the torque. Overtightening can damage the threads or break the screw.
For fine woodworking projects, it is recommended to use a hand screwdriver for final fine adjustments.
Installation Order and Alignment
For large structures (such as wood frames), it is recommended to secure key locations first, then gradually reinforce.
Ensure that screws are evenly distributed to avoid excessive localized force that could cause structural deformation.
5. Common Problems and Solutions
Wood Cracking
Cause: Failure to pre-drill holes or screws with too large diameters.
Solution: Pre-drill holes and tighten slowly and evenly.
Screw Stripping
Cause: Using an incompatible bit or low-quality screws.
Solution: Use the appropriate bit (e.g., Phillips, Hexagon) and avoid low-quality products.
Screw Rusting
Cause: Using ordinary screws in a humid environment.
Solution: Use galvanized or stainless steel screws and provide waterproofing.
Screw Loosening
Cause: Long-term stress on the wood or thermal expansion and contraction.
Solution: Add wood glue or use special expansion fasteners in the screw holes.
6. Maintenance and Safety
Regular Inspection: For structures such as wooden houses and terraces, check critical screws at least every six months.
Timely Reinforcement: Immediately address any loosening to prevent minor problems from becoming safety hazards.
Environmental Protection: Avoid prolonged exposure of the wood to moisture. Apply protective paint to extend the life of the wood.


 English
English русский
русский











 Products
Products Tel: 86-574-62101087
Tel: 86-574-62101087 E-mail:
E-mail:  Add: Xiaocao 'e Binhai Industrial Park, Yuyao, Zhejiang, China
Add: Xiaocao 'e Binhai Industrial Park, Yuyao, Zhejiang, China